Oral Glucose Tolerance Test and Diabetes Gestational
The purpose of a oral glucose tolerance test (or OGTT) is the measurement of the body’s efficiency in converting glucose into energy and this is important as energy for the body cells’ survival and growth comes mainly from glucose. This test is applied to diagnose pre-diabetes and diabetes. It is normally carried out to see if gestational diabetes has lead to diabetes.
Checking the possibility of getting gestational diabetes
The OGTT is carried out to check if gestational diabetes is present during pregnancy. The possibility of you getting gestational diabetes is greater if:
- You had gestational diabetes during an earlier pregnancy.
- You had a baby weighing heavier than 4.1 kg at birth during an earlier pregnancy.
- You have not reached the age of 25 and is overweight just before your pregnancy.
- You have already been diagnosed with prediabetes as well as diabetes.
see Gestational Diabetes – Diagnosis.
see What Seems To Cause Gestational Diabetes?
Preparing for a Glucose Tolerance Diagnostic Test
In order for you to be ready for the glucose tolerance diagnostic test, below are pointers on what you have to do before and during the test.
- For three consecutive days before the test, take healthy meals that give you carbohydrates weighing a minimum 150g each day. Recommended foods to supply you with sufficient carbohydrate are breads, fruits, grains, cereals, crackers, rice, potatoes, corn and beans.
- You must not drink, eat, smoke, not even perform any strenuous activity for a minimum of 8 hours previous to the first drawing of your blood at the start of the test.
- Inform your doctor on all nonprescription and prescription medicines you have been instructed to take. Before having the glucose tolerance diagnostic test, you may have to stop taking particular medicines.
- Activities and eating during the glucose tolerance diagnostic test can affect test results and so, they are not allowed. Therefore, you will only be allowed to drink only plain water and relax in a chair during the four hours required for the complete test.
It is important for you to discuss with your doctor on the necessity of having the test, whatever risks are involved and the conducting of the test. To get you to appreciate the necessity of the test, an information form on the medical test will have to be filled up by you.
How will gestational diabetes affect my labor and delivery, and my newborn? – Video Guide
How the Glucose Tolerance Diagnostic Test Is Done
Here are the steps taken during the testing:
- When you reach the venue of the test, some of your blood will be drawn. This blood is to be used to determine the level of fasting blood sugar. The result is the lowest point to be used for comparison with other sugar levels.
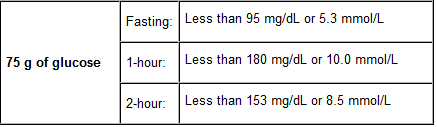
- Then, you have to take a certain amount of glucose in a drink. You are told to drink it as fast as possible. The amount of glucose you have to take may be either 75g or 100g. Pregnant women are told to drink 75g.
- Blood have to be drawn for tests at intervals of 1, 2, and perhaps 3 hours after drinking the glucose solution. For some, it is necessary to draw out blood for testing even earlier, half an hour to longer than the usual 3 hours from the time of drinking the glucose solution.
Getting a blood sample for the test
This is what the health care provider drawing out a blood sample will do:
- Wrap your arm between the shoulder and the elbow with a stretchable band to prevent your blood from through and, in the process, cause the vein to enlarge sufficiently to have a needle get access to the blood in it.
- Use alcohol to sterilize a site for the needle.
- The needle is pushed through the skin, into the vein at the site. There may be a need for a few needles.
- A tube is connected to the needle for collecting the blood sample.
- When sufficient blood has been drawn into the tube, the band can be taken off.
- Put a cotton ball onto the site for the needle while the needle is pulled out.
- Put some pressure on the needle site before bandaging the spot.
How It Feels like
Some patients have difficulty in drinking such a sweet glucose solution. They may experience nausea and vomit out the glucose solution. Vomiting will lead to the cancellation of your test, postponing it to another day. You may feel that the band tied around your arm for the collection of the blood sample is too tight. When it comes to the needle, some may feel no pain whatsoever while others may suffer a sudden sting or slight pain. The weaker patients be afraid of losing consciousness due to the number of blood samples drawn out of the body when, in actual fact, blood taken is so little, it will not lead to anemia.
Hardly Any Risk
For some people, their blood glucose levels are too low when the test is almost completed. However, there are times when feelings of low blood levels are experienced, they are found to be psychological as their blood glucose levels are, in fact, not low.
Nevertheless, it is important to know that the symptoms of hypoglycemia are sweating, hunger, weakness, hunger, and feeling restless or nervous or ; and if you experience them, you must check your glucose level immediately using a glucose meter. If your glucose level is indeed extremely low, the test has to be postponed to another day. Actually, there is hardly any risk from drawing out blood through a vein. The most you may suffer from is a mark indicating a small puncture with the needle. And if you do apply pressure on the spot for perhaps five minutes, even that mark cannot be seen. Although the vein can become infected after taking the blood sample, it hardly ever occurs. This infection is known as phlebitis and treatment given are warm compresses on the site a number of times each day.
For patients with bleeding problems, there can be too long a period of bleeding. Blood thinning medicines such aspirin and warfarin, can cause bleeding to be excessive. So, you should tell your doctor before the glucose tolerance diagnostic test if you use blood-thinning medicine and if you suffer from problems connected to bleeding and clotting.
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test Results
The OGTT determines how good the body is at using glucose as the principal supply of energy to its cells.
Normal
The normal values given, also referred to as a reference range, are merely a help to you. The ranges differ from one lab to another so, the lab you go to for your test may not have the same range as that given here for the normal values. However, in the report given by your lab should provide the reference range used by it. When evaluating the results of your test, your doctor has to take into consideration the state of your health and certain contributing influences. Thus, a test value in your report that is beyond the range for normal values listed here, may be considered still normal according to your lab’s own reference range. Where diagnosis of gestational diabetes is concerned, the ADA (American Diabetes Association) has suggested the usage of particular glucose values. So, accordingly, any glucose value greater than that given in the association’s table is an indication of gestational diabetes.
You are diagnosed with prediabetes, if two hours after starting the test, your oral glucose tolerance test result is 140 to 199 mg/dL.
High blood glucose levels
High blood sugar levels can be the result of hyperthyroidism, diabetes, and gestational diabetes. It can also be due to the effects of medicines like phenytoin (Dilantin), niacin, corticosteroids, some diuretics and those used for the treatment of high blood pressure, AIDS, or HIV. Excessive quantities of the hormone cortisol in the blood during Cushing’s syndrome can lead to high glucose levels too. Diseases such as Hemochromatosis, a genetic sickness, and pheochromocytoma can also raise blood glucose levels.
see High and Low Blood Glucose – Managing Your Levels.
see Hypoglycemia Vs Hyperglycemia.
Low blood glucose levels
Low blood sugar levels can be the effects of particular medicines used to treat diabetes, hypertension and depression. A lessened amount of cortisol and aldosterone in the blood due to Addison’s disease can bring about low blood glucose levels. Problems concerning the thyroid gland, the pituitary gland, the pancreas and the liver can also lead to low blood sugar levels. As a lot of health problems can alter your blood glucose levels, you doctor will have to go into any symptoms experienced and your health history if he finds any unusual results that warrants his concern.
see Blood Sugar During Pregnancy.
see Gestational Diabetes Testing.
What Affects the Test
Unless certain conditions are fulfilled, the test is not valid. In order for the test to be valid, smoking, alcohol, and the use of particular medicines like NSAIDs(nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), birth control pills, corticosteroids, seizure medicines, diuretics and those for hypertension have to be stopped for a certain period of time prior to the test. Those people with recent surgery, infectious diseases, illnesses, recent loss of weight as a result of a diet, and forced long bed rest due to a health problem should not take the tests as the results will not be valid.
Be prepared for further tests
If you are a diagnosed gestational diabetic, the possibility of you getting diabetes in later years is greater. Therefore, you are advised by the American Diabetes Association to undergo an oral tolerance glucose test for diabetes as well as prediabetes once in three years.